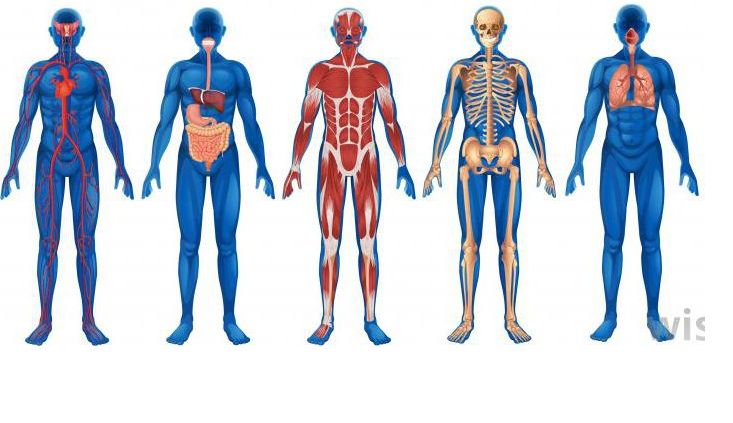
Anatomy
The human body is a single structure that is made up of billions of smaller structures of major kinds.
The basic structural and functional unit of the body is the cell. Each individual cell has a nucleus with different organelles embedded with a cell membrane.
Its the smallest unit of body capable of performing various functions in our body.
The major branches of science describe in detail about the structures and functions in the body.
The major structures of which body is framed up is the cell, with further combination making up a tissue and thus forming an organ with organ system.
Our body is made up of many types of tissues like the epithelial tissue for the skin, nervous tissue lining the nerves, muscular tissue for the muscles.
Our body is made up of different systems of the body for example: the digestive system, cardiovascular system, skeletal system, endocrine system etc.
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
The digestive system is the system concerned with the digestion and absorption of food with assimilation of the nutrients.
The Parts of Digestive System:
- Alimentary cannel – Is the passage through which the food passes from the stomach to the anus its parts are:
- Mouth
- Pharynx
- Esophagus
- Stomach
- Duodenum
- Jejunum-Ileum
- Caecum
- Colon
- Rectum
- Anus
- Organs – The organs included in the digestive system are:
- Liver and gall bladder
- Pancreas
- Salivary glands
Mouth
Is also called as Oral cavity or Buccal cavity.
The parts of mouth are:
- Cheeks-Formed by muscles
- Lips
- Teeth-32
- Gums
- Tongue
- Hard palate
- Soft palate
- Uvula
- Tonsil
Oesophagus:
- Is a Muscular collapsible tube.
- of Length-23 to 25 cm. It lies behind the trachea.
Stomach:
Is a muscular membranous bag, about 25 c.m in length, situated against the front wall of the abdomen, just beneath the diaphragm.
With the person standing straight the shape of the stomach is “J” letter shape. The larger part near the heart is the cardiac orifice. At the other end the stomach joins the duodenum at a narrow portion known as the pylorus.
Small Intestine:
Is a narrow tube about six meters long. It comprises three parts; the duodenum, the jejunum, and the ileum. It is coiled and twisted to allow it to fit into the abdominal cavity. The small intestine is lined with four or five million tiny, hair like projections called as villi. These provide an increase surface area for the digestion and absorption of food. The villi increase the surface area of the small intestine to about five times that of the skin. In the duodenum both the gall bladder and pancreas secrete their juices (bile and pancreatic enzymes). The second and third part of the intestine, the jejunum and ileum, lead from the duodenum to the large bowl (colon). Both jejunum and ileum secrete juices to aid in further digestion of food.
Large Intestine:
It begins at the caecum, passes up the right side of the abdomen (ascending colon), moves across the abdomen to the left side (transverse colon) and descends down the left side of the abdomen (descending colon). Its of length 5 feet and diameter of 2.5 inches.
Its name changes from colon to the rectum in its last part of pelvis. It ends in the anus. The lining of the large intestine secrets mucous, but no destive enzymes. The function of large intestine is formation of the faeces and absorption of water.
Faeces are formed partly from bowel secretions and partly from bacteria. These faeces are thrown out from the anus.
Parts for Digestive Enzymes
- Salivary Glands
- Stomach
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Small intestine
Salivary Glands
There are three types of salivary glands:
- Parotid
- Submandibular
- Sublingual
The function of these glands are; theysecrets –
- Mucin – Liquifies food.
- Ptylin – Acts on starch. It hydrolyzes starch into disaccharides. Even food goes in stomach the action of ptylin proceeds.
Gastric Juice. It contains
- Water –
- Pepsin – It transforms protein into peptone.
- Renin – Helps to digest milk protein.
- HCl – Destroys bacteria.
- Maintains PH.
Thus avoids fermentation
Bile and Pancreatic juice
- Bile – It helps in digestion of fat. It makes food alkaline.
- Pancreatic juice – is of three types
- Trypsin – It converts peptone into amino acids.
- Amylopsin – it converts Carbohydrates into Disaccharides. [Sucrose, Lactose, Maltose]
- Lipase – It converts fat into fatty
pH of juices
- Saliva – 6.5
- Stomach – HCl – 2 to 3.
- Pancreatic – 7.1 to 8.2
- Bile – 7.6 to 8.4
- Intestinal – 7.6
Intestinal juice
- Pepsin – It converts peptone into amino acids.
- Lactose – It converts bisacrides into Glucose.
- Lipase – It converts fat into fatty acids.
Liver
- Largest organ in the body which is Brown coloured. It is 1.4kg weight
- It Lies in right hypocondrium. Protected by ribs.
- Contains two main lobes-right and left. Each lobe contains various lobules. Each lobule contains hepatic cells ,vein artery sinusoids and bile canaliculi
Functions of Liver are:
- Storage of sugar, vitamin A. and D.
- Formation of bile.
- Detoxification.
- Metabolism of unwanted proteins.
- Formation of prothrombin, fibrinogen.
- Formation of heparin.
Time period for Digestion of food:
- In mouth – Few seconds.
- In esophagus – Few seconds.
- Stomach – 2 to 4 hours.
- Small intestine – 3 to 6 hours.
- Large intestine – 3 to 10 hours.
The period of digestion depends upon –
- Nature and quantity of diet.
- Frequency of intake.
- Digestion of previous
Process of Digestion:
The food after chewing is swallowed enters the oesophagus and the enters the stomach almost half of the digestion takes places in the stomach and then the semi digested food enters the small intestine where it mixes with other juices from the liver and pancreas then the rest of the digestion takes place in the small intestine.
The food is then passed to large intestine from where the waste solid matter in form of faeces is thrown out of the rectum. This way the process of digestion is completed.
Asana plan for the digestive system
- Padaottanasana
- Padachakrasana
- Padasanchalana
- Pawanmuktasana
- Paschimottanasana
- Ardhamatsendrasana
- Dhanurasana
- Urdhva dhanurasana
- Mayurasana
- Hamsasana
- Ek pada koundinyasana
KRIYAS FOR DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
- Shankprakshalana
- Kunjal kriya
- Pranayama for healthy digestive system
- Anuloma vilom
- Sheetali
- Bhastrika
- Mudras for healthy digestive system
- Apana mudra
- Samana mudra
For More Information Click Here: Yoga Teacher Training in India