RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
The Respiratory system is the system through which we breathe. The process of respiration is accomplished through thereby breathing in and out.
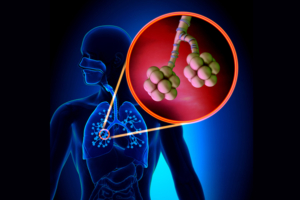
The Respiratory system is made up of two main components the respiratory tract and the thoracic cage.
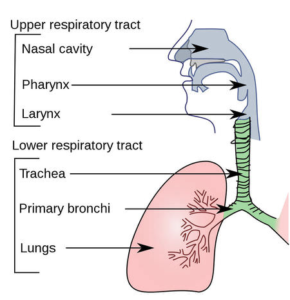
1) Respiratory tract – is a long tract which has nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree and lungs.
2) Thoracic cage – Is made up of Sternum, Ribs, Vertebrae.
3) Muscles involved in respiration are – Intercostal muscles, abdominal lmuscles and muscles of the neck.
4) Diaphragm.
Parts of respiratory tract
Nose:
It has following parts:
1) External part of cartilage and skin
2) Septum
3) Bony part [Chonca]
4) Nasal cavity
5) Mucus membrane and cilia
6) Hard palate
Specific curve and tissue helps in protection and warming of air.
Pharynx:
This funnel shaped cavity is the next part just behind the nose and is Common passage for air and food.
Its divided into 3 parts –
1) Nasopharynx
2) Oropharynx
3) Laryngopharynx
Tonsils are in the pharynx
Larynx:
Is a short cartilaginous tube joining pharynx with the trachea; together with vocal cords within the larynx. It has a vital role in speech production.
Trachea:
It’s the tubular passage for air [wind pipe].
12 to 15 cm long and 2.5 cm in diameter.
Formed by c shaped cartilages [16 to 20] which are joined to each other by muscle fibers.
Due to cartilage it always remains open.
Inside the trachea is Ciliated epithelium that helps to trap up the foreign particles and solid mater.
Bronchi:
Trachea divide into 2 main bronchi, called as primary bronchus, each.
Primary divides into secondary and tertiary branches.
The branching is called as Bronchial Tree.
Last division is Bronchioles each bronchiole enters into alveolus.
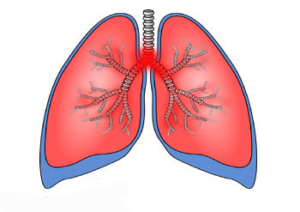
Lungs:
The human body has two lungs the Right which has 3 lobes and the Left which has 2 lobes.
Each lobe contains numerous alveoli.
Each alveolus is like a balloon.
And each balloon is covered by net of capillaries.
Lung is covered by pleura. [Partial and visceral]
Mechanism of respiration :
Respiration comprises of two processes –
1) External Respiration- This comprises of
Inspiration means breathing in.
Expiration means breathing out.
2) Internal [cellular] – This process of respiration takes place at the internal level of lungs
Taking oxygen from blood and giving carbon dioxide.
Movements during Inspiration
1) Contraction of external intercostals.
2) Increased A. P. diameter of thoracic cage.
3) Ribs and sternum moves upward and outward.
4) Diaphragm contracts and goes downward.
5) Relaxation and stretching of abdominal muscles.
Movements during Expiration.
1) Contraction of internal intercostals
2) Decreased A.P. diameter
3) Streunm goes slightly backward
4) Diphragm relaxes and comes upward
5) Abdominal muscles contracts
Control of Respiration:
1) Takes place from the part of the brain called as Medulla oblongata also known as Respiratory center.
2) Chemical – Carbon di oxide and other.
Respiratory Rate: The rate at which we btreathe varies depending upon the physical work out and age.
In resting position.it is in following range per minute.
Newborn baby – 40 to 45.
1 year child – 30
2 to 5 year child – 24.
Adult – 14 to 16.
Vital capacity of the Lung
It is measured through the volume of the air that we can inhale and exhale very deeply.
It is the sum of inspiratory and expiratory volumes.
Practice of Asana and Pranayama increases lung capacity
Lung capacities
- Tidal volume – 500ml
- Inspiratory reserve volume – 3100
- Residual volume – 2400ml
- Total lung capacity – 6liters
- Vital capacity – 4800ml
ASANA PLAN
- URDHVA HASTASANA
- VIRABHADRASANA
- ANJANIASANA
- GOMUKHASANA
- PURVOTTANASANA
- ARDHAMATSENDRASANA
- PARIVRITT JANUSIRSHA ASANA
- CHAKRASANA
- MATSYASANA
- PRANAYAMA OR BREATHING TECHNIQUES
- NADI SHODHANA
- ANULOMA VILOM
- VILOM PRANAYAMA
To Know More About Click Here: Yoga Teacher Training in India